[ad_1]
Do you want to rank higher on search engines?
Then, plain old SEO techniques aren’t enough anymore. The days are gone when selecting keywords and stuffing them into a content piece was enough to make it rank.
Thanks to the ever-changing Google algorithms, SEO has evolved a lot. Local SEO, advanced SEO, off-page SEO, and lately, semantic SEO are shifting the paradigm.
Semantic SEO is the recent development to cope with Web 3.0 assets. It is a new chapter in the search engines evolution book, which has made user intent paramount.
But, it often confuses people, causing digital marketers to have sleepless nights as they try to figure out how to rank higher using semantic SEO.
So, to clear all mist around the topic, we have compiled this guide to help you understand semantic SEO better.
What is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO refers to the use of semantics (the meaning of words and their relation to one another) in optimizing a website for better search engine visibility.
Basically, for semantic SEO, you need to consider a topic instead of a keyword when looking for content ideas. This means your content marketing plan must revolve around the user intent to provide in-depth information about the search query.
Earlier, content creators used to track top-performing keywords and include them multiple times in a content piece. This was a good old blog SEO technique as it worked back then.
Today, an average person spends about 10 hours online. That means people are consuming more online content.
That also means you have more avenues to showcase your content to prospects than before. All you need is a chance. And that chance is what semantic SEO offers.
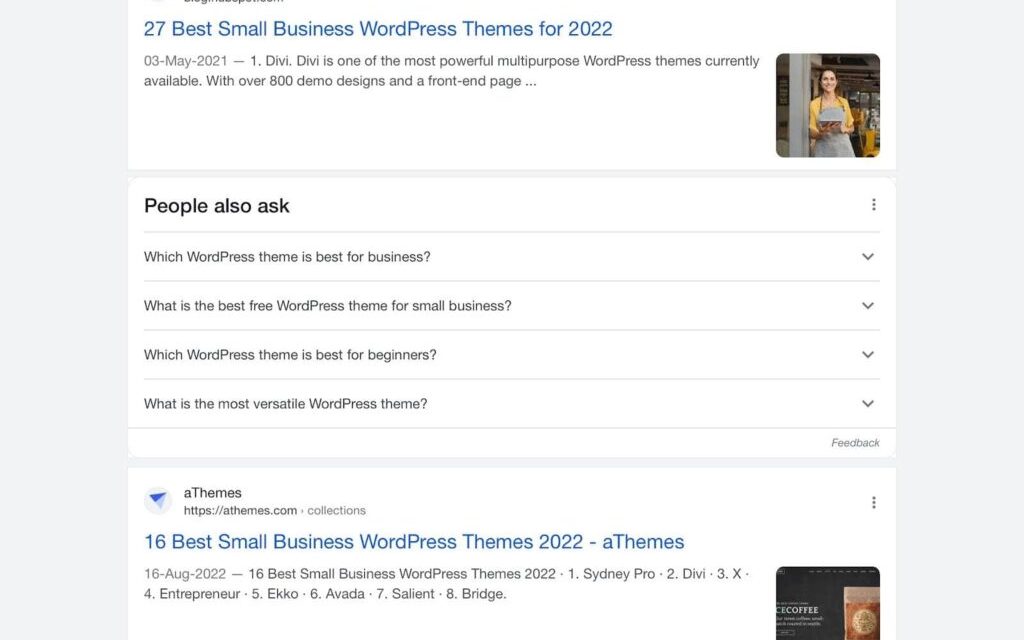
Let’s say you searched for the “best WordPress themes for small businesses” on Google. You will not only get results for the searched keyword but also for related questions that might interest you. For example:
- Which WordPress theme is best for business?
- What is the best free WordPress theme for small businesses?
- Which WordPress theme is most popular?
- What is the best WordPress theme for beginners?
All of these related questions come under the scope of semantic SEO. Answering these questions in your content can help you provide in-depth information to users.
Let’s Teardown Google’s Semantic Search Approach
Google is the leading search engine with over 270 million unique visitors in the U.S. only. It is one major reason behind the development of semantic SEO.
If you want to rank your website in Google Search results, it is essential to understand how Google’s semantic search approach works to evaluate the relevance of different pieces of content.
Let’s see the factors behind Google’s semantic search approach.
Knowledge Graph
The knowledge graph is a large and systematic knowledge base that Google uses to understand the relationships between particular entities and concepts.
A knowledge graph has several entities that describe real-world entities like places and people. Further, these entities form the graph nodes. The common entities are movies, local businesses, etc.
For example, when you search for “best story books for children,” the results that appear at the top are due to a knowledge graph result.

The Hummingbird Algorithm
Google’s Hummingbird algorithm was the first tap on semantic SEO. This algorithm uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to ensure that web pages displayed in search results match the context of the search query and not just some keywords.
After this update, SEO experts suggested using more LSI keywords to make your web page rank higher against the pages with fewer relevant keywords.
For instance, when we search for the term, “business automation,” we get videos, local services, and top companies that provide business automation along with the standard results.

This is what you get with the Hummingbird update — complete knowledge.
The RankBrain Algorithm
Two years into the Hummingbird algorithm, Google launched RankBrain in 2015. It is a machine learning system that functions as a smart AI query analysis and a ranking factor.
RankBrain, like Hummingbird, attempts to understand the user’s goal or intent behind the questions they ask on Google. The main difference between them is RankBrain’s AI component.
RankBrain is constantly picking up, investigating, and searching for similarities between the pages that clients find important.
The BERT Update
The BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) update was introduced by Google in 2019. This focuses on getting additional data and setting up a discussion-oriented search.
BERT enables users to easily find and discover significant and precise data. It employs NLP (Natural Language Processing) technology to improve understanding of search queries, interpret text meaning, and identify relationships between words, phrases, and so on.
These changes intend to improve the computer’s understanding of the search query context. It is a comprehensive machine analysis of words and intentions.
How Does Semantic Search Work?
Semantic search is a method that search engines use to understand the contextual meaning and intent behind a search query. It aims to provide search results that align with your search intent.
Simply put, semantic search focuses on why you type and search for a particular keyword and what kind of results you want to achieve through it.
Many people confuse semantic search with Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI). But, semantic search is a lot more than LSI; that only tells the content’s intent.
To better understand semantic search, you have to learn about factors that contribute to it, such as:
A User’s Search Intent
As the name suggests, the term, “search intent,” refers to the reason behind searching for something online.
Why are you Googling a specific thing?
Usually, people search for something because they intend to buy, learn, or find it. Thus, when we search for “cloud storage,” Google gave us generic results like what cloud storage is, how it works, etc.

But, when we specify our intent using keywords like the “best cloud storage solutions,” Google shows rich sources, top cloud storage tools, etc. to give more precise results.

So, the copywriting tip here is to create content around topics that users search for. If your content is excellent but not related to something that users search for, you will not get your website ranked.
Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are focused on providing more direct information to users. It highlights excerpts of content that appear at the top of a Google search results page in what is known as “position 0.”
Here’s an example:

Voice Search
According to Google, 25% of people use voice search every day. Voice search is more direct, natural, and simple. Therefore, to improve your SEO score, you need to optimize your content for voice search, as it is a big part of semantic search.
An easy way to do so is to optimize your content for conversational keywords.
Rich Results
Rich results take your Google experience beyond clicking on the blue anchor text. It uses structured data to enrich your search results with images, videos, carousels, and other non-textural elements.
For example, if you search for a recipe, Google also shows you results like:

These are known as “Rich results or Rich snippets.” They feature information like photos, user ratings, preparation time, and the ingredients you’ll need.
Users are more likely to click on the pages featured in these Rich snippets instead of the normal search results.
The Benefits of Using Semantic SEO
Google simply wants insightful and valuable content for its users. It wants to provide a complete solution to users in one place.
Using semantic SEO will give you the opportunity to create comprehensive pieces of content with multiple internal links, keywords, and information.
So, when you create rich content that users are searching for, you can gain the following benefits:
Higher Search Rankings
The whole purpose of this blog post is to show that using semantic SEO can help improve your search engine rankings. So, let’s talk about this benefit for a bit.
Semantic SEO helps improve your search engine rankings in several ways. First of all, it allows you to create long-form content pieces. A study showed that blog posts beyond 2000 words hold the top 10 positions in Google’s search results pages.
Besides this, publishing a longer, in-depth guide about a topic sends Google the signal that your website is credible and authorized in that area. It helps improve your organic search engine rankings.
Rank for More Keywords
With long-form content, you have the opportunity to include different keywords in each piece of content. For example, you can use different LSI keywords in subheadings and tags to rank your page for potential keywords.
Take this Salespanel blog post, for example.
It is about the “top 10 website visitor tracking tools” but this blog post did not only discuss the best website visitor tracking software solutions. It also talks about what website tracking is, its benefits, and why you may need it.

Salespanel included several different related keywords in this blog post. As a result, it helped them establish brand authority and provide users with a complete solution for “website visitor tracking.”
Help Your Visitors Stay Longer On Your Website
The content created using a semantic approach helps you retain web visitors for longer. Foremost, your well informative content can hold users on your website for a more extended period.
Secondly, you can add several internal links to direct visitors to other relevant pages and posts on your website. This way, a visitor will stay longer on your website.
A longer dwell time means that a visitor will have more chances to explore your products or solutions, and they might even buy them.
Feature Your Content in the “People also ask” Section On Google
The “People also ask” section in Google search results is a golden place to get your content featured. Under this section, Google shows short answers related to a user’s search query.
For example, if a person wants to learn about “indoor lighting,” Google also answers questions like:

As you can see, a post by Consumer Reports got featured as the answer to the first related question.
If you can make it, featuring in the “People also ask” section is a direct way to reach your potential customers.
To do this, you need to cover your topic in detail.
According to Ahrefs, 43% of all searches now show this box. So, this semantic SEO strategy can increase your website traffic significantly.
8 Semantic SEO Strategies to Improve Search Engine Rankings
Semantic SEO is different to traditional SEO.
While traditional SEO is more keyword-focused, semantic SEO focuses on the user. It revolves around creating content that meets the needs of the user behind searching for specific information.
Therefore, you cannot optimize your content for semantic SEO using old methods like keyword stuffing. Instead, you need to use more analytical and data-driven strategies to improve your search results rankings.
Here are some strategies that can help you improve your website’s search rankings by leveraging semantic SEO:
1. Conduct Comprehensive Keyword Research
Semantic SEO doesn’t focus on keywords but on the topic as a whole. But, this doesn’t mean keywords are no longer important to optimize your content for better search rankings.
In fact, you need to broaden your keyword research criteria. Instead of focusing on a couple of keywords related to your business, you need to concentrate on intent-based keywords that might interest your users.
To do so, you can use keyword analytical tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, Moz, etc.
Don’t just stick to search engine-related tools. Today, every social media channel is a search engine in itself. It can help you find keywords related to targeted audience intent. So, you must also use social media analytics tools to dig deeper into your audience’s minds.
Once you have a collection of significant keywords, you can use a keyword clustering strategy to optimize your content. Since Google doesn’t limit how many keywords you can use in your content, it gives marketers an opportunity to rank one page for several competitive keywords.
Keyword clusters refer to grouping similar or related keywords. This strategy can help you expand on a particular topic and target multiple keywords per page.
For example, CloudTalk is a call center automation software solution. They target multiple topics on different keywords to improve their search rankings. These include:
- Call center software
- Cold call tips
- Cold calling
- Sales in a call center
- Communication strategies
- Sales in a call center
- Sales call script
- Call pops

So, the bottom line is that keywords are still essential for search engine optimization. You just have to target more relevant, search-related keywords for your topic.
2. Understand User Intent
As we have already discussed, semantic SEO is all about understanding user intent. Therefore, it is focused on why a person searches for something online and what more they would like to know about the topic.
So, simply targeting random keywords will not work anymore. It will only throw your content into the ocean without life support.
For example, targeting the keyword, “SMM panel,” will give you an SMM panel definition, listicles featuring the best SMM panel tools, and whatnot.

You might get unnecessary competition from websites and brands without any direct connection with your website. But, when you optimize your topic based on user intent, you can reduce the search competition and put your content in front of the right audience.
3. Optimize Titles and Meta Descriptions
Keyword-optimized content titles and meta descriptions are a crucial part of every successful SEO strategy. They can help search engine crawlers index and rank your content for relevant keywords.
Since semantic SEO is not focused on a keyword, you have to mention clear intent in the content. Your title and meta description must cover all of the topics covered in your content.
Suppose, a person wants to know how to buy Instagram followers. They will check out the titles and meta descriptions of different search results to evaluate which link might offer them the information they’re looking for.
Let’s take a look at the search results displayed below.

While the highlighted HubSpot post doesn’t exactly address the keyword, it covers something that users need to know before they decide to buy Instagram followers. In addition, it also includes advice from experts.
This is why Google has ranked their post along with ranking the list of websites that allow you to buy Instagram followers.
4. Write In-Depth Content Pieces
“Go big or home” is the approach you must adopt when writing semantic content.
Your post must cover all of the relevant subtopics that a user might need to know about. But this doesn’t mean that you can just dump all of the information in your content mindlessly.
You should use properly organized subheadings and visuals to make your content readable and engaging.
You can use an SEO content assistant like Surfer to ensure that your content includes all NLP-suggested words and phrases and other synonyms/variations of the keyword.
However, if you don’t want to use the tool, simply go to Google and pick heads from the “People also ask” section. This section practically has all of the related topics that people search for online.
So, select all of the relevant queries and answer them in your content. The more insightful content you write, the greater your search rankings, traffic, and conversions will be.
5. Add Internal Links On Contextual Anchor Text
When a user lands on your website, they are looking for the most straightforward and best solution to their problem.
If they have to spend time searching for the information they need, they will most likely move on to another website. And, negatively impact your search rankings.
That is why you should provide them with as much relevant and contextual information as possible about the topic. In addition, you should also include internal links to other related posts on your website.
A solid internal link structure can do wonders for your website’s dwell time, traffic, and bounce rate. It is much better than putting all of the information on one web page.
However, you’ll need to use relevant anchor text in a way that compels readers to click on them to hunt for more information.
6. Use HTML Tags Efficiently
Another important semantic SEO strategy is to create an outline for your article using relevant HTML tags.
You should break down your article into a few major sections and then break them into smaller subsections. Then, tag these sections using heading tags to make it easier for Google to understand your content’s structure. This includes:
- H1 heading tag – for the title
- H2 heading tags – for main headings
- H3 heading tags – for subheadings
While H2s and H3s are often enough, you may also consider using H4s for further subheads.
However, I suggest that you use bullet points to make your content readable under different headings.
You should also highlight important phrases and lines using text styles like bold, italics, or underline tags. This helps both search engine crawlers and readers to find information faster.
Assume the title of your article is “BBQ Chicken Pizza.” Then, your article’s main sections (H2 headings) could be:
- BBQ chicken pizza recipe
- Best restaurant for BBQ pizza
- Health concerns with eating chicken pizza
- Best time to eat a BBQ chicken Pizza
Research each of those topics as if they were the topics of a different article. When you take this approach, you can ensure that your piece of content has topical authority and is more authoritative than the other articles on the same subject.
7. Add Structured Data Markup
Use structured data to help Google better know your content (schema). It’s a format for categorizing content on a page.
Structured data is a language that tells search engines what content to show appealingly. It allows you to easily convey your article’s subject, description, image, video, type, ratings, reading minutes, and so on.
It helps both users and search engines understand your content better.
You can create structured data for your content using Schema.org. It provides a framework for describing what your content means and how it relates to other elements on your website.
At the very least, using schema will assist search engines index your content more accurately. Using structured data may help your pages rank higher in organic search results and also feature in Rich snippets (which we discussed earlier with a “recipe” example.
8. Create Topic Clusters
A topic cluster is a collection of pages centered on a single topic. The main hub is a pillar page, with cluster pages linking to and from it.
First, you will publish content on a specific topic. Then, on that same topic, publish a few more blog posts.
For example:
If you want to create content on, “Best Small Business SEO Strategies,” your pillar post can briefly mention subtopics like:
- Benefits of small business SEO
- Off-page SEO techniques for small businesses
- On-page SEO techniques for small businesses
- SEO tools for small businesses
- Digital marketing tips for small businesses
Then, you can write and publish separate articles or guides on each of these subtopics, and link them to your pillar content.
Topic clusters are useful for semantic SEO because they tell search engines that your website is an authoritative source on the subject. Furthermore, internal linking generated by a topic cluster sends an important topical significance signal to search engines.
That’s the reason why popular publishers like Backlinko have created content hubs for topics like “SEO Marketing.”

It has a cluster of articles related to:
- SEO fundamentals
- Keyword research
- Content optimization strategies
- Technical SEO
- Link building
- User experience signals
- SEO tools and software
- Advanced SEO strategies
- And more
Wrapping Up
Now that you understand what Semantic SEO is, how it works, and how to optimize your website for semantic search, it’s your turn to implement all of the strategies we discussed.
You can use them to make your content more insightful, rank for more keywords, and significantly improve your search rankings and search traffic.
So, what is holding you back?
Start now by creating semantic search-friendly content for your website. Hopefully, you’ll soon see a boost in your rankings.
guest
[ad_2]
Source link